Gums can recede to the point where teeth become loose and eventually fall out, typically when the recession reaches 5mm or more and significant bone loss occurs. Early intervention is crucial to prevent further deterioration. If you notice signs of gum recession, consult a dentist immediately to avoid severe consequences.

Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back, exposing more of the tooth or its root. This process can be gradual, making it difficult to notice until severe symptoms develop. Unlike general gum disease, which affects the entire gum structure, gum recession specifically involves the loss of gum tissue, often leading to sensitivity, aesthetic concerns, and, in extreme cases, tooth loss.
Several factors contribute to gum recession, including:
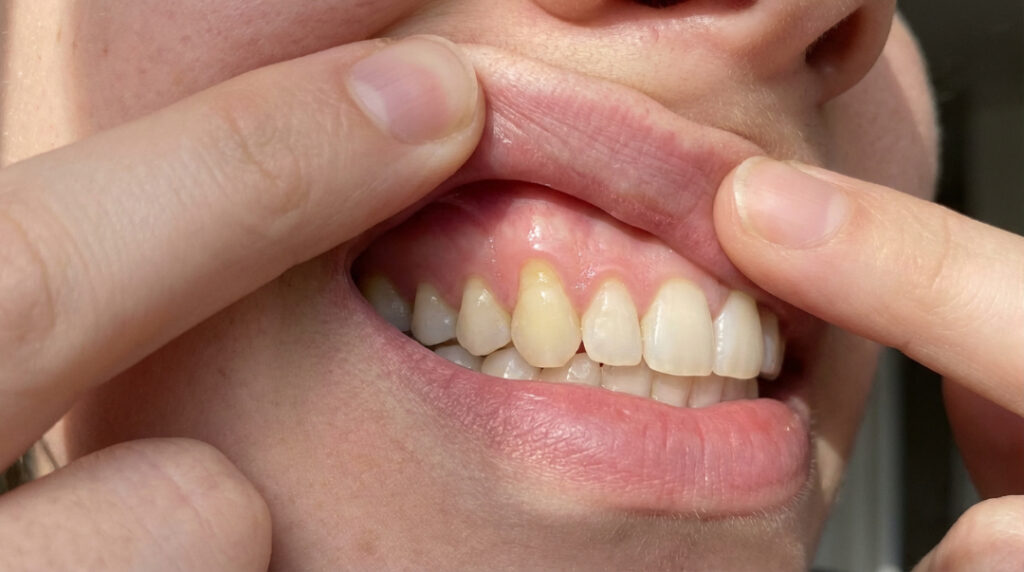
Gum recession progresses through several stages, each increasing the risk of tooth instability and loss.
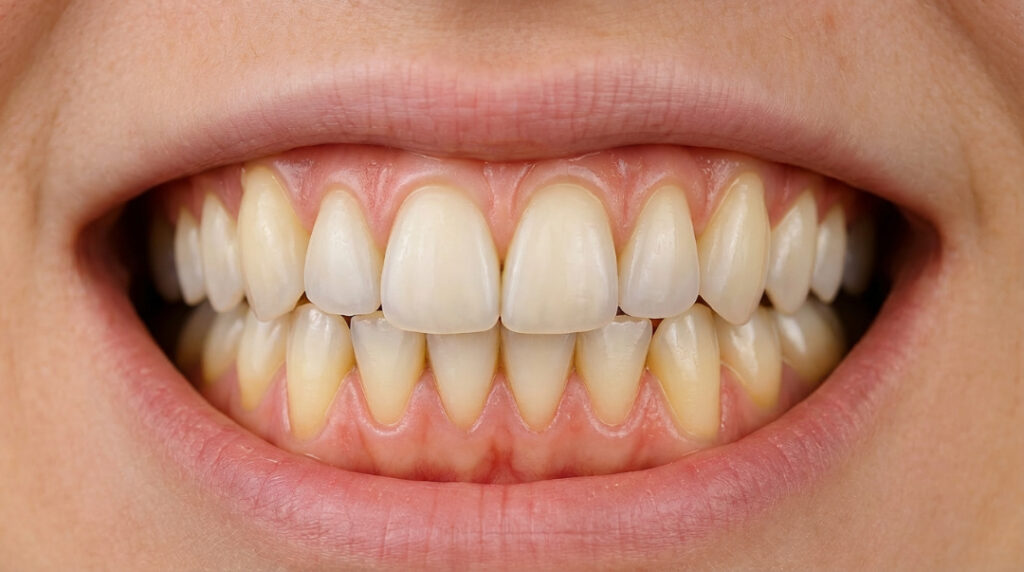
Tooth longevity with gum disease largely depends on how far the gums have receded and the extent of accompanying bone loss. Teeth typically become loose and fall out when gum recession reaches 5mm or more, combined with periodontal deterioration.
As gums recede, the underlying alveolar bone may also deteriorate. This bone supports the teeth, and when it breaks down due to gum disease, the teeth lose their foundation and become loose. Advanced periodontal disease is often irreversible and requires immediate dental intervention.

While gum tissue does not grow back naturally, certain steps can slow or halt the progression of gum recession.
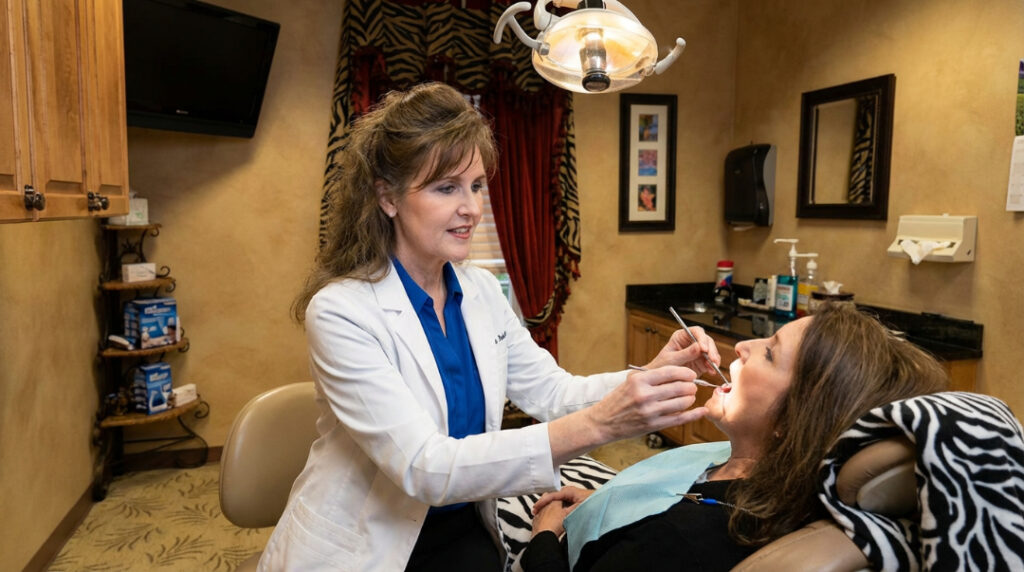
If gum recession is already severe, several treatments can help restore gum health and prevent tooth loss.
Once gum tissue is lost, it does not regenerate naturally. However, certain treatments like gum grafting can restore lost tissue. Future advancements, such as stem cell research and regenerative medicine, may provide new solutions for gum tissue restoration in the coming years.
New advancements in dental care continue to improve gum recession treatment. Some promising innovations include:
Gum recession is a progressive condition that, if left untreated, can lead to tooth loss. When recession reaches 5mm or more, teeth become unstable due to bone deterioration. Early intervention is key—whether through proper oral care, lifestyle changes, or professional treatment.