TLDR:
Yes, pineapple juice may help reduce swelling after wisdom teeth removal due to bromelain, an enzyme with anti-inflammatory properties. However, it’s not a miracle cure—moderation is key, and it should be used alongside proven recovery methods.

If you’ve been scrolling through social media lately, you’ve likely seen the viral trend: people drinking large amounts of pineapple juice before wisdom teeth removal to reduce swelling and pain. But does pineapple juice really help with wisdom teeth recovery, or is this just another internet myth?
At Buford Dentist, we’ve been closely following the science behind this claim. While pineapple juice contains bromelain—a natural anti-inflammatory enzyme—there’s more to consider than a trending TikTok video. Let’s dive deep into the facts.
After removal, it’s common to experience:
Most recoveries follow this timeline:
Standard post-surgical advice includes:
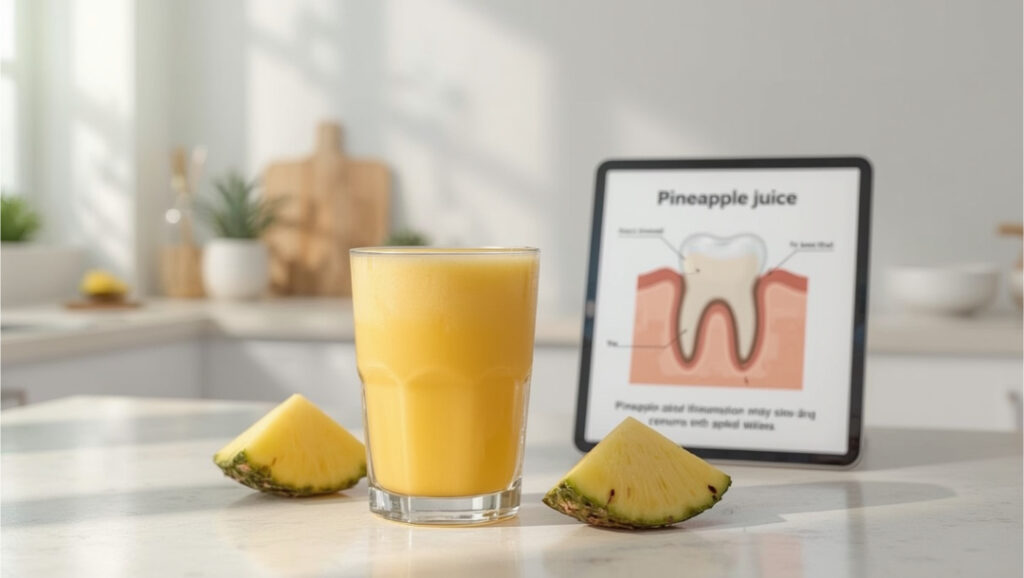

So, while there is promising science behind bromelain, the effectiveness of pineapple juice specifically is still uncertain.

Drinking large amounts of pineapple juice (some TikTokers suggest 64 oz a day) comes with real risks:
Dental professionals, including those at Buford Dentist, recommend limiting pineapple juice intake and watching for these signs.

If you’re curious about trying pineapple juice as part of your recovery:

While pineapple juice may play a supportive role, it should not replace proven post-surgery healing tips. Here are core practices you shouldn’t skip:
Eat soft, soothing foods that are easy to chew and won’t irritate your extraction sites:
Avoid: